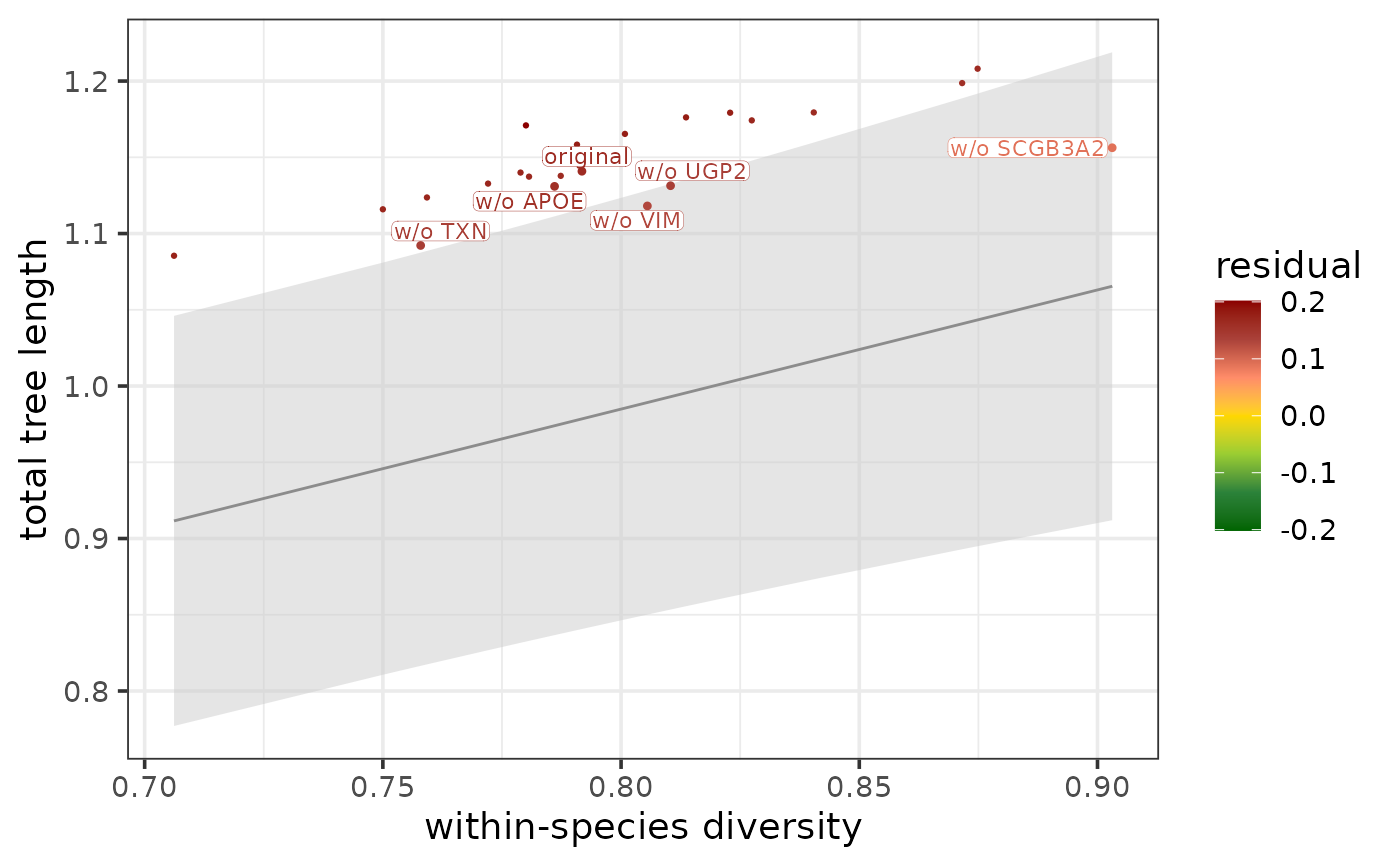
Plots the cross-species conservation of target genes within a conserved/diverged module and marks the targets that are particularly responsible for the conservation/divergence.
Usage
plotConservedDivergedTargets(
target_conservation,
N = 5,
label = "auto",
colors = NULL,
font_size = 14
)Arguments
- target_conservation
Data frame of cross-species conservation measures for each jackknife version of a module.
Columns required in case the focus of interest is conservation and overall divergence:
- focus
Character, the focus of interest in terms of cross-species conservation, "overall" if the focus of interest is conservation and overall divergence.
- regulator
Character, transcriptional regulator.
- type
Character, module type (orig = original, jk = jackknifed or summary = the summary across all jackknife module versions).
- id
Character, the unique ID of the module version (format: nameOfRegulator_jk_nameOfGeneRemoved in case of module type 'jk', nameOfRegulator_orig in case of module type 'orig' and nameOfRegulator_summary in case of module type 'summary').
- gene_removed
Character, the name of the gene removed by jackknifing (NA in case of module types 'orig' and 'summary').
- total_tree_length
Numeric, total tree length per jackknife module version.
- within_species_diversity
Numeric, within-species diversity per jackknife module version.
- fit
Numeric, the fitted total tree length at the within-species diversity value of a jackknife module version.
- lwr_fit
Numeric, the lower bound of the prediction interval of the fit.
- upr_fit
Numeric, the upper bound of the prediction interval of the fit.
- residual
Numeric, the residual of the jackknife module version in the linear model. It is calculated as the difference between the observed and expected (fitted) total tree lengths.
Columns required in case the focus of interest is species-specific divergence:
- focus
Character, the focus of interest in terms of cross-species conservation, the name of a species if the focus of interest is species-specific divergence.
- regulator
Character, transcriptional regulator.
- type
Character, module type (orig = original, jk = jackknifed or summary = the summary across all jackknife module versions).
- id
Character, the unique ID of the module version (format: nameOfRegulator_jk_nameOfGeneRemoved in case of module type 'jk', nameOfRegulator_orig in case of module type 'orig' and nameOfRegulator_summary in case of module type 'summary').
- gene_removed
Character, the name of the gene removed by jackknifing (NA in case of module types 'orig' and 'summary').
- {{species}}_subtree_length
Numeric, the subtree length of a species per jackknife module version.
- {{species}}_diversity
Numeric, diversity within the species of interest per jackknife module version.
- fit
Numeric, the fitted subtree length of the species at the diversity value of a jackknife module version.
- lwr_fit
Numeric, the lower bound of the prediction interval of the fit.
- upr_fit
Numeric, the upper bound of the prediction interval of the fit.
- residual
Numeric, the residual of the jackknife module version in the linear model. It is calculated as the difference between the observed and expected (fitted) subtree length of the species.
- N
Integer, the number of top conserved/diverged target genes to label.
- label
Character, specifies which data points should be labelled. If "auto" (default), in case of a conserved module the top N least conserved jackknife module versions (most conserved targets) are labelled, while in case of a diverged module the top N least diverged jackknife module versions (most diverged targets) are labelled. If "conserved", the top N most conserved targets are labelled, and if "diverged", the top N most diverged targets are labelled, regardless of the degree of conservation of the module as a whole. If "both", both the top N most conserved and the top N most diverged targets are labelled.
- colors
Character vector, the colors to visualize the residuals. The vector can contain any number of colors that will be passed on to and converted into a continuous scale by
scale_color_gradientn.- font_size
Numeric, font size (default: 14).
Details
To determine whether a module as whole is conserved, diverged overall or diverged on a specific lineage, the CroConet approach relies on module trees reconstrcuted from pairwise preservation scores between replicates and statistics calculated based on these trees (total tree length, overall within-species diversity, subtree length and diversity of each species). To identify individual genes that contribute the most to conservation/divergence, the same statistics can be used in combination with jackknifing. For more details on the approach and the generation of the target_conservation object please see findConservedDivergedTargets.
The function plots each jackknife version of a module along the regression line that captures the relationship between total tree length and within-species diversity (in case the focus of interest is conservation and overall divergence) or between the subtree length and diversity of a species (in case the focus of interest is species-specific divergence). The residuals compared to this regression line characterize the cross-species conservation of the different jackknife module versions and the corresponding absent target genes: the jackknife version that has the highest residual is the most diverged, therefore the corresponding target gene is the most conserved, while the jackknife version that has the lowest residual is the most conserved, therefore the corresponding target gene is the most diverged.
The regression line is drawn in dark grey, and the 95% prediction interval of the line is shown as a light grey area. The jackknife module versions are colored by their residuals: the red to yellow part of the color spectrum denotes positive residuals, while the yellow to green part of the color spectrum denotes negative residuals (the entire spectrum always spans residuals from -max(abs(residual)) to max(abs(residual)) across all jackknife module versions of the module of interest).
In case of a conserved module, the lightest green data points are typically the most interesting: these correspond to the smallest negative residuals, i.e. the least conserved jackknife module versions with the most conserved target genes removed. Analogously, in case of a diverged module, the lightest red data points are typically the most interesting: these correspond to the smallest positive residuals, i.e. the least diverged jackknife module versions with the most diverged target genes removed. In an extreme scenario, the least conserved jackknife module versions of a conserved module can reach positive residuals (red color) and the least diverged jackknife module versions of a diverged module can reach a negative residuals (green color). However, this should be rare if we assume that the divergence/conservation of a module cannot be contributed to a single target gene, but it is rather the combined signal of all targets together.
As a default, in case of a conserved module, the top N least conserved jackknife module versions (most conserved targets) are labelled, while in case of a diverged module, the top N least diverged jackknife module versions (most diverged targets) are labelled. Using the parameter label, it is possible to manually choose whether the most conserved targets ("conserved"), the most diverged targets ("diverged"), or both the most conserved and most diverged targets ("both") should be labelled. The gene name in the label always refers to the target gene removed in the given jackknife version (format: "w/o {{geneName}}").
In addition to the jackknife module versions corresponding to the most conserved/diverged target genes, the function always labels the original module version as well where no target gene was removed. The original module is always labelled as "original".